Infrastructure
Overview of AEIS Assets
AEIS Infrastructure Highlights
Pipeline
AEIS’s assets are near major pipeline infrastructure, including the newly announced reversal and upgrade to NGL transport of the Tennessee Gas Pipeline. Further opportunities include a short extension to connect to the ATEX ethane pipeline (currently operating), a reversal and upgrade of the Texas Eastern pipeline (within 10 miles of the site), and a modification of the proposed Buckeye Express (also within 10 miles of the site) from a dry gas line to an NGL pipeline. Providing access from gathering and processing areas of the Utica/Marcellus region to the hub, while greatly reducing transportation costs and decreasing ethane rejection rates.
Water
The Ohio River provides waterway access to the northeast and Gulf coast. Access to large amounts of water for solution mining and hydrofracking requirements is a key aspect of site location. The Ohio River and other locales offer close access to large supplies of water required for world class level operations. AEIS has the footprint to potentially offer subsurface storage options to handle the waste materials from these nearby activities.

Workforce
A substantial base of human capital is required for building and operation of the storage hub. The tri-state region of Ironton, Ohio, Huntington, West Virginia, and Ashland, Kentucky are among the metropolitan areas with the industrial background experience. The project will promote significant job creation and economic development.

Transportation
The area is also serviced by a major interstate (I-64), US 52, a four-lane divided highway, Ohio State Route 93, Lawrence County Route 26, and Ohio State Route 650. These roads are lightly traveled and large vehicle habitable. In addition, the Norfolk Southern Railway system passes within a few miles of the site, providing for potential rail distribution.
Market Perspective & Defined Hub
Charts & Graphs
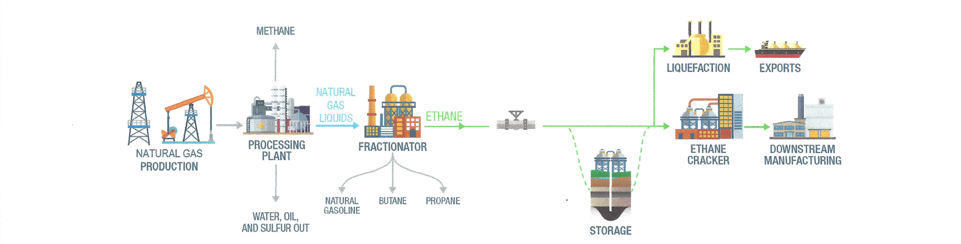
The following discussion examines the kinds of physical assets typically present in a NGL hub. When pertinent, Appalachia-specific examples for physical NGLs infrastructure development are cited. This then discusses what a trading hub is, how trading happens, and various ancillary benefits generated by these activities. This section also provides a look at existing NGLs trading in Appalachia and ends with a descriptions of three existing North American NGLs.
In addition to infrastructure enabling commodity flows and demand response, energy hubs feature an array of financial activities and relationships involving multiple parties. Such parties include commodity producers and consumers, transportation and logistics service providers, hub operators, legal service providers, financial institutions, traders, and regulators. This confluence of activities and actors shapes the market dimensions of a hub and the relationships between and among the parties involved become more complex when physical and financial commodity transactions occur. An energy hub engenders economies of scale in resource utilizations, information sharing, and innovations, which, in aggregate, enhance the hub’s value over time. Energy hubs and the activities shaping them are also highly visible, allowing them to attract potential participants and investments in infrastructure and the commodities traded there.
A market hub is a center of activity that facilitates various kinds of transactions involving one or more commodities. Market hubs can be categorized into three main categories: transit hubs, trading hubs, and transition hubs.105,106 The unique characteristics of an individual hub and how it functions depend on several factors including its geographic location, infrastructure asset base (including access to storage), development history, and state of maturity. Not all hubs will grow to become benchmark trading hubs, i.e., ones that set the reference price. In general, benchmark hubs attract significant trading volumes because they are used for both physical balancing of supply and demand and portfolio risk management; conversely, non-benchmark hubs engage in physical balancing of supply and demand and are used by shippersto adjust and balance their respective physical portfolios.
Transit hubs are key transit or trans-shipment points whose chief role is to facilitate the transport of NGLs. They are important in the physical context of NGLs deliveries entail a network of physical infrastructure for storing and moving NGL commodities in and out of the hub. NGLs transit hubs are found inConway, Kansas; Hattiesburg, Mississippi; and Napoleonville, Louisiana.
A transit hub may reach a high level of interconnectedness with other hubs or demand/supply centers through pipeline, rail, marine, and/or other transportation modes. The Conway, Kansas, NGLs hub is a case in point. It holds sizable salt cavern storage capacity, offers third-party access, and has a highly interconnected system of pipelines with other regions yet serves mainly as a transit point for NGLs commerce. From Conway, propane is sent north to meet highly seasonal demand ranging from crop drying (Midwest) to home heating (Midwest and Northeast), or south to satisfy Gulf Coast petrochemical and export demand; butanes move to Conway from producing regions and Midwest refineries, and are either stored to satisfy seasonal demand for gasoline blending in the region or shipped to the Gulf Coast for export or in-region consumption; ethane also either passes through Conway on its way to the Gulf Coast, where it is consumed as a petrochemical feedstock or exporter, or to Midwestern petrochemical plants as a feedstock. There is not much local demand for NGL processing and/or end use in the immediate vicinity of Conway, but the hub’s interconnectedness with Midwestern demand centers, Midcontinent and Rockies production, and the Gulf Coast NGL complex make Conway central in the logistics of NGL.
Disclosure
Our partnerships acknowledge and disclose that this website was created using publicly available internet resources. The respected institutions mentioned herein are the best at what they do and we appreciate their efforts. The representations throughout this website combines the research and opinions, accessed through publicly available information associated with said institutions.
